Estate Planning: Cut Taxes & Secure Legacy
For affluent individuals, estate planning involves more than merely transferring assets; it is about developing a plan that reduces tax burdens while ensuring that your heritage reflects your desires. The solution lies in utilizing specialized instruments that extend beyond simple wills to safeguard wealth across generations.

Irrevocable Life Insurance Trusts (ILITs)
ILITs eliminate life insurance benefits from your taxable estate. By placing policies into the trust, the death benefit can be received by heirs without tax implications. Additionally, you may contribute to the trust using annual gifts that take advantage of the gift tax exemption to pay premiums, transforming life insurance into a tax-favorable legacy mechanism that circumvents both estate and income taxes.
Grantor Retained Annuity Trusts (GRATs)
GRATs facilitate the passing of assets that gain value, like shares, real estate, or equity in companies, to beneficiaries while facing low gift tax obligations.You allocate assets to the trust and receive a fixed annuity for a designated time, with any appreciation above the annuity amount passing to beneficiaries free of taxes. This approach is beneficial for assets expected to significantly increase in value as it locks in lower gift tax valuations from the beginning.

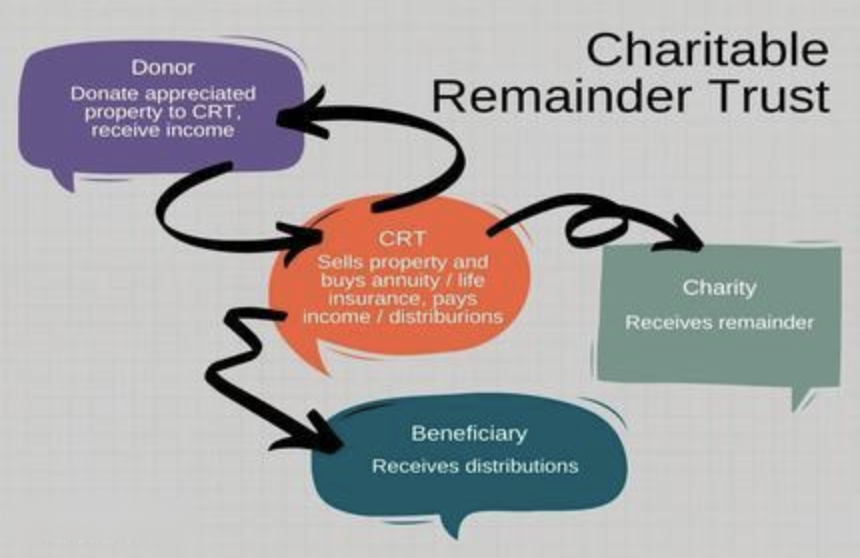
Charitable Remainder Trusts (CRTs)
CRTs combine charitable contributions with tax benefits. When you give assets to the trust, you earn a consistent income for life or for a specified period, while the remaining assets will be donated to charity. This strategy reduces your taxable estate, provides an immediate charitable deduction, and allows you to evade capital gains taxes on the sale of appreciated assets within the trust, making it suitable for those holding significant low-basis investments.
Family Limited Partnerships (FLPs)
FLPs allow you to transfer business or investment holdings to family members while still maintaining control. By gifting limited partnership shares, you can use valuation discounts related to lack of control or marketability to lessen the gift tax responsibility. Heirs will gain ownership, but you retain management power, ensuring the assets are overseen according to your preferences.
Qualified Personal Residence Trusts (QPRTs)
QPRTs enable you to pass your main residence or vacation home to heirs at a lower gift tax cost. You can continue living in the property without paying rent for a designated duration before it transfers to beneficiaries. The gift tax value is calculated based on the property’s present worth minus the value of your living rights, which reduces the taxable gift and protects future appreciation from estate taxes.
Annual Gift Tax Exclusion Strategy
By maximizing annual gifts, which is $18,000 per recipient in 2024, you can gradually transfer wealth over time. You can gift cash, stocks, or even partial real estate shares. For families, gifting to both spouses and children can multiply the exclusion amount—in an example, a couple can give a total of $72,000 yearly to a child and their spouse—thereby decreasing the taxable estate incrementally.
Achieving successful estate planning relies on proactive and customized methods. By integrating trusts, family dynamics, and intricacies of tax regulations, wealthy individuals can transfer their wealth with minimal tax repercussions, ensuring that their legacy is preserved as they desire.
(Writer:Hoock)


