How Bitcoin Works
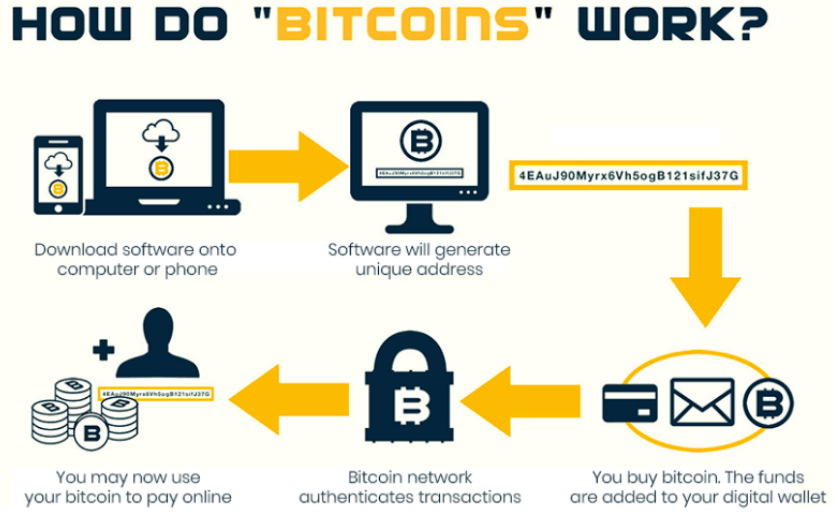
If you want to try Bitcoin trading, as a beginner, the first thing you need to do is install a digital wallet on your computer or mobile device. It is not difficult to set up this wallet. It is a free open-source file that will generate your first and subsequent Bitcoin addresses. There are currently three types of Bitcoin wallets, including software wallets (on personal computers), mobile wallets (on mobile devices), and web wallets (on a Bitcoin service provider's website).
Bitcoin uses public key encryption to ensure security. It means that when a new Bitcoin address is created, its cryptographic protection mechanism will contain a public key and a private key, both of which will consist of a long string of letters and numbers.
Each address holds some Bitcoin balance, so all you need to do is get a Bitcoin wallet and deposit your bitcoins into it. You can obtain coins through various methods, such as buying from Bitcoin exchange centers like Mt.Gox or Bitstamp, or through the BitInstant service to exchange between Bitcoin and traditional currencies.
Please note that all Bitcoin transactions are public and permanently recorded on the Bitcoin network, which means that your Bitcoin account balances and transactions are visible to everyone. Therefore, it is recommended that Bitcoin holders set up a separate address for each transaction to keep the account private and secure. Once you have your Bitcoin address and coins, you can make online payments at companies that accept Bitcoin as payment. The company will send you the address of their Bitcoin wallet, into which you can deposit the amount of Bitcoin you need to pay. After you've made a payment to that address, the transaction will complete within seconds, although the subsequent verification may take ten minutes or more.
All Bitcoin transactions, without exception, appear in a public transaction ledger, also known as Blockchain. This is to confirm that the Bitcoin payer actually owns the money and to prevent fraud and double payments.
Why are transactions taking so long to validate? This is due to the complex algorithms involved in Bitcoin mining, which can take a while to decode, even if your computer is extremely powerful.
Suppose you have made an online payment with a company called BitChamp, and you need to transfer money from your Bitcoin wallet to the company's Bitcoin wallet. The detailed transaction steps are as follows:

BitChamp creates a new Bitcoin address and you need to send money to this address. A private key (visible only to BitChamp) and a public key (visible to you and everyone else) are generated. Just like you don't need to show your identity information to merchants when shopping in cash, you don't need to reveal your real identity in transactions with BitChamp, and you can make anonymous payments. Through the Bitcoin client (that is, the free Bitcoin software installed on your computer), you transfer 5 coins in your Bitcoin wallet to the BitChamp address, which is the transaction information. The Bitcoin client will enter the private key at the address where you initiated the transaction, and since your public key is visible to everyone, no signature verification is required. Your transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network and will be verified within minutes. Your five coins will also be transferred from your account to the BitChamp address at this point.
Please note that the first two steps of the transaction require the involvement of you and/or the seller, while the last two steps are performed automatically by Bitcoin's client software and the Bitcoin network. At the same time, it is crucial to keep your private key in a secure address, because anyone who gets your private key can take control of your Bitcoin at that address and spend it fraudulently.
(Writer:Susan)



